 LROSE is a joint project between the Atmospheric Science Department at Colorado State University (CSU) and the Earth Observing Laboratory (EOL) at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is funded by the US National Science Foundation (NSF).
LROSE is a joint project between the Atmospheric Science Department at Colorado State University (CSU) and the Earth Observing Laboratory (EOL) at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is funded by the US National Science Foundation (NSF).
LROSE is hosted in the Remote Sensing Facility (RSF) and the code is freely available on Github under a BSD-style license and on the LROSE main page. Documentation and other aids, such as 'starter kits', are on the LROSE Wiki. Data is stored in portable data formats, based on UNIDATA NetCDF, following the Climate and Forecasting (CF) conventions to facilitate data assimilation by models.
The overall goal of the project is to provide high-quality, open source software to the community of scientists, researchers, educators, and operational organizations using atmospheric lidars, radars, and profilers. LROSE builds upon a core framework which was developed over a number of years prior to the start of the project. Building upon this base framework, functionality has been added that is seen as a high priority by the user community. The goal is to keep the software up-to-date, relevant, easy to use, and robust. Testing is carried out at CSU, EOL, and in the user community.
LROSE core software components
Since the scope of software for radar and lidar is large, the software is organized into modular libraries and applications. The size of the modules in LROSE is chosen to keep the software maintainable, while also keeping the number of modules reasonable.
LROSE is intended to handle information at all stages:
- raw time series data at the instrument in native format
- moments data in radial coordinates
- algorithms in radial coordinates
- products in Cartesian coordinates
- engineering displays
- science displays that integrate with other data sets for visualization
- provision of QC data to models for data assimilation
The software in the lrose core contains all of these components, as depicted in the following schematic:
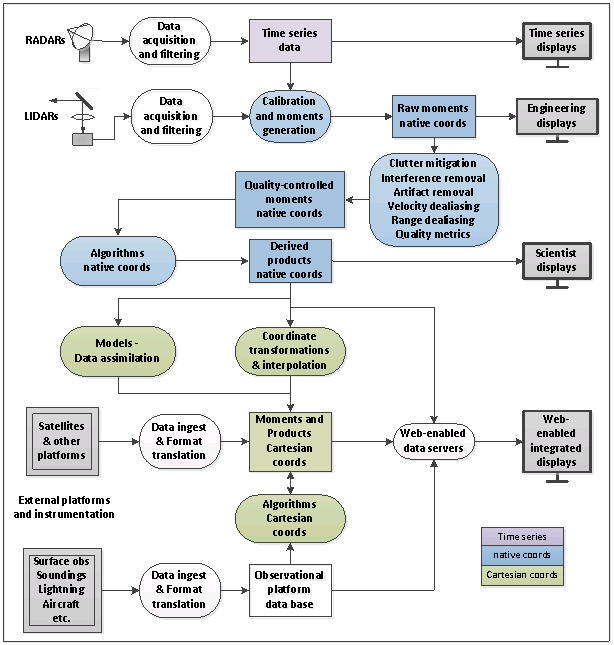
As part of the LROSE project, NCAR/EOL is upgrading and refactoring some of the core, and adding functionality as required.
Releases
The LROSE development proceeds on a calendar year basis. The major release for each year, starting in 2018, is named after a variety of rose. Within the calendar year there are 4 minor releases, specifically at the end of March, June, September and December.
| Year | Major release | |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Blaze |  |
| 2019 | Cyclone |  |
| 2020 | Elle |  |
| 2022 | Topaz |  |
| 2022 | Jade |  |
| 2024 | Colette |
|
LROSE core software and documentation
LROSE uses GitHub to host the software releases, documentation, and other resources.
Overall LROSE site: http://lrose.net/
Wiki: http://wiki.lrose.net/index.php/Main_Page
Core LROSE software: https://github.com/NCAR/lrose-core
Other LROSE software
Examples of current and legacy LROSE software that is not included in the core releases:
- EMERALD (thE Matlab™ Environment for Radar And Lidar Data). A Matlab based viewer for CfRadial radar and lidar data.
- CEDRIC (multi-radar Doppler Wind Analysis). Legacy software.
- REORDER (radar-to-Cartesian transformation). Legacy software.
- Solo II and Solo 3 (display and editing of radar and lidar observations). Legacy software.
